Radioactive Decay
Anything that releases energy is considered radioactive. An example of this is from Isotopes, “each of two or more forms of the same element that contain equal numbers of protons but different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, and hence differ in relative atomic mass but not in chemical properties; in particular, a radioactive form of an element.”(Oxforddictionaries) When an isotope becomes unstable, it will slowly release the extra energy until the atom becomes stable again. This is called radioactive decay. Although we know that a radioactive atom will decay, we can’t predict when it will decay. Scientists use “half life” to find out the amount of time the atom will decay to half of its original atom. An example of this is Uranium 238, it has a half life of about (4.468×10^9 years) which is about 4.468 billion years, it decays into thorium-234 by alpha decaying. There are three different types of radioactive decay, they are : Alpha decay, Beta decay, and Gamma decay. When an atom is releasing energy. they are all considered ionizing, which is a radiation that has the energy to remove electron from an atom, also able break bonds. Gamma decay is the most powerful out of all of them, beta decay comes in second, and alpha decay is the weakest.

Alpha decay (Particles)
Alpha decay is the most common type decay. Found in heavier elements that has a atomic number greater than 52.
-
They decay by shedding alpha particles, alpha particles are helium nucleus that has 2 protons and 2 neutrons .
-
When it decay, the mass number of the atom will decrease by 4 and atomic number will decrease by 2, changing the atom.
-
Alpha decay occurs in decaying heavy element such as: uranium, thorium and radium.

Beta decay (particles)
-
there are two kinds of Beta decay β+ and β-
2. β+ decay occurs when an proton changes into a neutron, releasing a positron and neutrino. Equation (p Æ n + e+ +n.)
3. β- decay occurs when a neutron decays into a proton, realeasing an electron, and an antineutrino. Equation(n Æ p + e - +.)
4. Beta decay occurs in an environment where the amount of neutrons is overwhelming the amount of protons, which is commonly found in nuclear reactor plants.
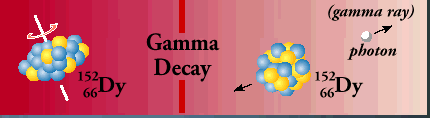
Gamma decay (Electromagnetic waves)
a. Gamma decay is the decay with the highest frequency, higher than the Beta and Alpha decay. It emits gamma rays, which is the highest type of rays in the ER,.
b. During a gamma ray, the atomic nuclei changes from high energy to low energy by emitting high energy photons through electromagnetic waves with extremely short wavelengths.
c. The photon released during a Gamma decay contains neither mass or charge, energy released during Gamma decay are pure energy from the nucleus of the atom.